

Interpretation and analysis of qualitative data occur simultaneously, in an iterative process. This paradigm is often associated with qualitative research. The goal of research conducted according to the constructivist paradigm is to understand how individuals construct their own reality.
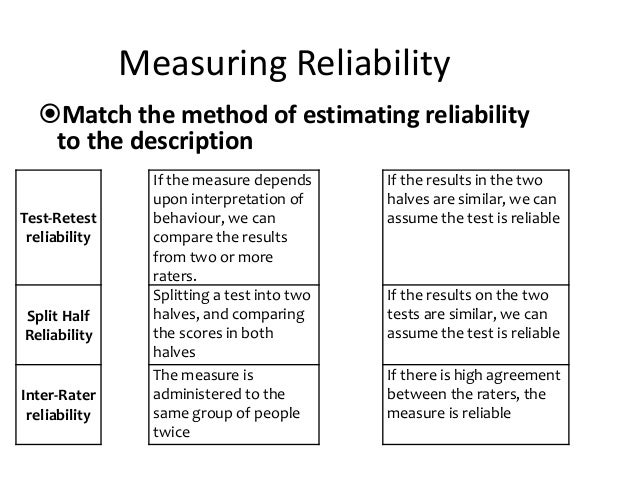
In the constructivist paradigm, multiple interpretations of reality exist. Qualitative studies are well suited to generating causal hypotheses, but not to testing them. Interpretation in qualitative studies sometimes yields hypotheses that can be tested in more controlled quantitative studies. Which of the following is characteristic of qualitative research? Select all that apply.Ī) It is consistent with the constructivist paradigm of inquiry.ĭ) It involves an iterative process of interpretation and analysis. A correlation is the association or relationship between variables. The term generalizability, used in quantitative research, is analogous to the term transferability in qualitative research, which is the extent to which qualitative findings can be transferred to or have applicability in other settings or groups. Lincoln and Guba (1985) created standards for the trustworthiness of qualitative research that parallel the standards of reliability and validity in quantitative research. NSF Consulting Pty Ltd.The term trustworthiness in qualitative research parallels which of the following terms used in quantitative research? Select all that apply. Types of reliability and how to measure them. Steps are taken to make sure the work’s findings are the result of experiences and ideas of the informants, and that evaluation findings are arrived at by considering solid evidence. The processes within the study are reported in detail, so that a future researcher can repeat the work Is it important to consider the findings of the study within the broader context of other people and settings, and whether similar projects and methods conducted in different environments would be of value. Reliability in qualitative research: Credible The same test conducted by different people.ĭifferent versions of a test which are designed to be equivalent. Reliability in quantitative research: Test-retest the measurement could apply to others/the same result would happen each time.the extent to which a research instrument consistently has the same results if it is used in the same situation on repeated occasions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
